The working principle of the inverter generator
The variable frequency generator(Inverter generator) connects and assembles the generator’s stator and rotor through bearings, bases and end covers to achieve operation. An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. Inverters come in many different sizes and shapes, depending on the source and power output. They are commonly used in applications such as solar systems, vehicles, and portable electronics.
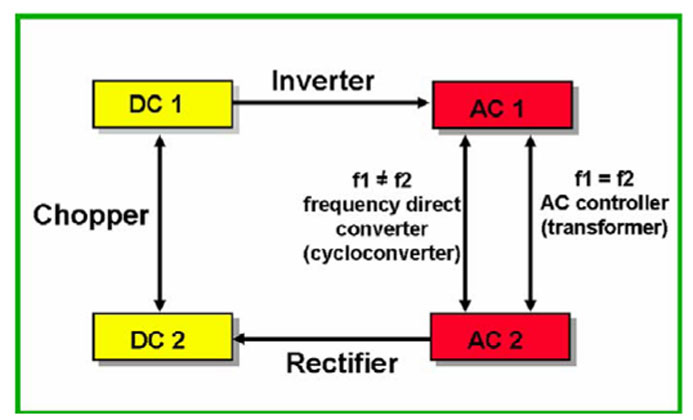
The working principle of the inverter generator is by converting the input direct current into adjustable alternating current. The following is the basic working principle of a variable frequency generator:
DC input: The variable frequency generator first receives the input of DC power. This is usually provided through the generator’s control system, which can be a battery or external power supply, etc.
Inverter conversion: The input DC power passes through the inverter, which is one of the core components of the variable frequency generator. An inverter converts direct current into adjustable alternating current.
Frequency adjustment: The inverter can adjust the frequency of output AC power according to needs. This means that different frequencies of power output can be produced as required.
Voltage Regulation: In addition to the frequency, the inverter also regulates the voltage of the output AC. This allows the inverter generator to provide power output at different voltages.
Output power supply: The regulated AC power is supplied to external equipment or electrical systems through the output port of the generator to meet the needs of various application scenarios.
How do traditional generators work?
The working principle of a generator is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators work by using the mechanical energy provided by an internal combustion engine to rotate a coil or armature around a magnet. As the coil rotates, a magnetic field is created and a current is induced in the armature. The current is then passed through a rectifier, which sends the resulting DC power to the output, where it is converted into an AC output.
The generator’s output can be used to power a variety of devices and appliances, from cell phones to computers to lights. Generators are often used in areas without reliable power, such as in remote areas or during power outages.

Compared with traditional generators, variable frequency generators can adjust frequency and speed, and their application range is wider. A variable frequency generator uses a frequency converter to change the rotation frequency of the generator to different levels in order to output the required power voltage and frequency. The rotation frequency of the variable frequency generator can be adjusted to an appropriate value to meet the needs of different electrical equipment and has a wide adjustment range.
long life: Variable frequency generators have a long service life, because adjusting the frequency through the frequency converter can improve the operating efficiency of the generator when running under different loads and extend the service life of the equipment.
Good stability: pure sine wave output, variable frequency generator output voltage and frequency are stable, which can meet application scenarios with high power quality requirements.
Wider application range: Variable frequency generators can be applied to various load requirements and can be widely used in industrial equipment, agricultural equipment, construction equipment and other fields.
Precise control: The variable frequency generator can perform precise speed and power control according to actual needs, providing more stable and reliable power support for other equipment.
Low noise: Since the speed of the variable frequency generator can be adjusted, noise and vibration can be reduced, reducing interference to the surrounding environment and users.
High efficiency: At the same time, the machine uses a permanent magnet motor. Under the same power level, the output power of the permanent magnet generator is twice as high as that of the excitation generator at idle speed; the permanent magnet generator has no carbon brushes and no slip rings. The structure eliminates the radio interference caused by the friction between the carbon brush and the slip ring; eliminates electric sparks, is particularly suitable for working in environments with a high degree of explosive danger, and also reduces the generator’s requirements for ambient temperature.
Therefore, according to the different working principles of the inverter generator and the traditional generator, combined with the usage scenarios, it is easy for the user to make a choice whether to choose the inverter generator or the traditional generator.









